feel man is one of the frequently used command along ls and cd commands in Linux. Have some more which you think we use frequently then post it in comments. Many people who are new to Linux do not know its potential. They just read a man page for a specific command and go away or just use “man commandâ€. This post is mainly meant for newbies to Linux/Unix. Do you know there are other commands which are similar to man command? Below are the list of commands which I call cousins to man pages.
Other helpful manuals available in Linux
- info
- help
- –help
- which
- where
To know more about these commands you should visit my other post on them.
As I said man(abbreviation to manual) command is useful to read more details about any command you want.
Example 1: Get information about passwd command such as what it do, options available, examples to use it, related commands etc.
man passwd
This will be opened in a default file viewer, most of the Linux distributions use less as default editor. To exit from man pages use “qâ€.
Example 2: As I said man pages are opened in a default viewer, if you want to change that use -P to change to some other viewer. Below example uses cat command for viewing man pages.
man -P cat passwd
Example 3: How about reading man with man pages. We can do that with following command.
man man
This post is about details displayed from above command(man man) output.
Example 4: There is a perception that man pages are written only for Linux command. That is not true. We have man pages written for normal commands, admin commands, configuration files, concepts etc. Below is the list of man categories.
Man pages types in Linux
1 Executable programs or shell commands 2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel) 3 Library calls (functions within program libraries) 4 Special files (usually found in /dev) 5 File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd 6 Games 7 Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7) 8 System administration commands (usually only for root) 9 Kernel routines [Non standard]
If you see there are total 9 type of man pages available. This number varies on different flavours of Linux/Unix. What that means for you? Let me explain with an example.
Suppose you want to know more about passwd command in Linux we just give man passwd. But if you want to learn more about /etc/passwd file format then you have to use man 5 passwd. Both command outputs are different, see it your self by using below examples.
man <catagory-number> <keyword>
Example:
man 1ssl passwd
man passwd
man 5 passwd
All above commands will give you different information depending on category where they fall.
Where are my man pages located?
Example 5: All the man pages are located in /usr/share/man. If you want to know where a perticular man page located use whereis commnad
whereis passwd
Output:
passwd: /usr/bin/passwd /etc/passwd /usr/share/man/man5/passwd.5.gz /usr/share/man/man1/passwd.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/passwd.1ssl.gz
If you observe output, we have different man pages(man5, man1, man1) located in different locations. These corsponds to man page types which we seen in above example.
Example 6: Not liking all the man pages in short and bit confused about the output, use -w for finding location of a man page.
man -w <type> command
Example
surendra@sanne-taggle:~$ man -w 5 passwd/usr/share/man/man5/passwd.5.gz
Example 7: Want to display all these commands in single command instead of using man 1, man 5 etc? Use -a for that.
man -a passwd
Example 8: How about viewing multiple man pages for different commands at same time. You can use man command to append commands.
man ls pwd whoami
The Linux man page categories
Each man page is categorised in to different sections for easy use. Suppose if you want just basic options use first section or if you want learn about each option in detail use second section.
Below are the common categories(not necessary all or in the same order) we see in most of the man pages.
NAME -One line answer about what this command do. This is the same output we see inwhatis command output.
Read Full Post: http://www.linuxnix.com/understand-man-pages-in-linux/
 This week in Linux news, The Linux Foundation’s senior director of security, Emily Ratliff, ranks among Business Insider’s list of the “Most Powerful Women Engineers,” The Open Mainframe Project announces new areas of focus, and more! Stay informed with these recent top Linux headlines:
This week in Linux news, The Linux Foundation’s senior director of security, Emily Ratliff, ranks among Business Insider’s list of the “Most Powerful Women Engineers,” The Open Mainframe Project announces new areas of focus, and more! Stay informed with these recent top Linux headlines: Greg Kroah-Hartman has just announced earlier today, February 26, 2016, the general availability of the third maintenance release in the stable, long-term supported Linux 4.4 kernel series.
Greg Kroah-Hartman has just announced earlier today, February 26, 2016, the general availability of the third maintenance release in the stable, long-term supported Linux 4.4 kernel series.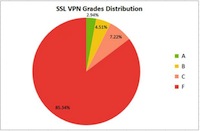 Information security firm High-Tech Bridge has conducted a study of SSL VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and discovered that nine out of ten such servers don’t provide the security they should be offering, mainly because they are using insecure or outdated encryption.
Information security firm High-Tech Bridge has conducted a study of SSL VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and discovered that nine out of ten such servers don’t provide the security they should be offering, mainly because they are using insecure or outdated encryption. The Ubuntu Release Team has announced the availability of new beta test images for select community editions. The new development release, which carries the designation 16.04 Beta 1, is recommended for testers only and is not considered suitable for daily use.
The Ubuntu Release Team has announced the availability of new beta test images for select community editions. The new development release, which carries the designation 16.04 Beta 1, is recommended for testers only and is not considered suitable for daily use.