All the Operating Systems that we use now-a-days, either Windows or an Open Source platform like Linux, comprise of various sets of programs and events that keeps running in the background to carry out the tasks to maintain efficient and reliable use of system resources. These events may happen in system software, for example the init process, or user applications such as Apache, FTP and others.
Now the question that arises in everyone’s mind is – how to keep an eye on working state of the system and different applications that are running in the background? One of the general solutions is that the system administrator himself keeps a review on the Log-files on a daily basis from the Production Environment.
But is this really a productive and easy factor to check each Log file on a daily basis which involves reviewing each log file from several system areas and applications. Still it is possible but making a user available at daily basis is not always a possible task. Here come the Log software management tools into action. They help to monitor, review, analyse and even generate reports from different log files as configured by a System Administrator.
Whether it’s a brand new car or just a Chipotle burrito, free stuff makes you happy. The same goes here with these Log management software as all of these are free to download and easy to manage. We have put together a list of the best free Log management software solutions out there for you to compare and contrast accordingly to you needs.
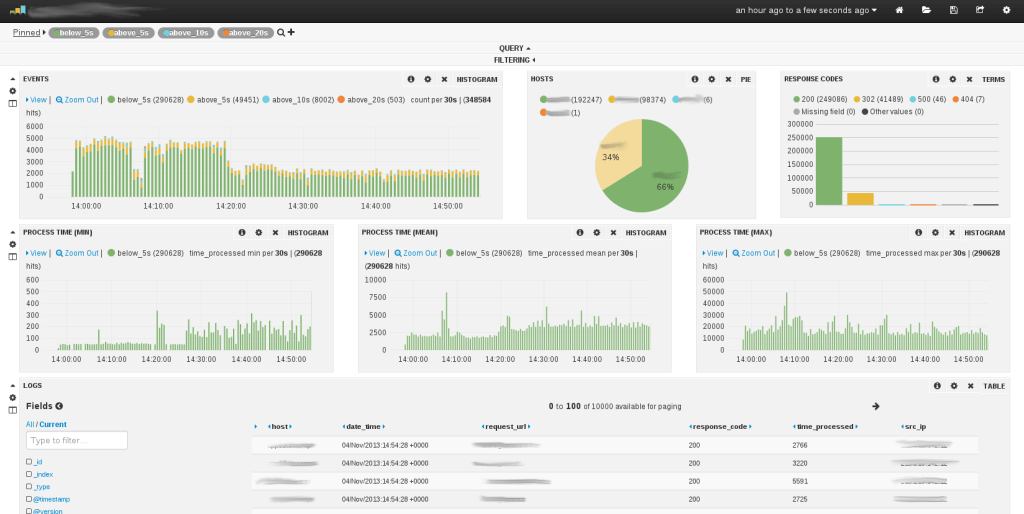
1. Graylog 2.
Being a fully integrated Open Source Log management software Graylog 2 enables a user to collect, index, and analyse both framed, systematic and disorganized data from any available source systems. Apart from this, the tool helps in running analytics, alerting, monitoring and powerful searches over your whole log base.
Its web interface is designed in Ruby on Rails while the server is programmed in Java. All of the source code can be accessed through Github.
When it comes to Features. Graylog 2 consist of following features
1. More Reliable due to its Features
2. Enabled with dashboard and a notification system
3. Can work from any log source
4. Real time log processing
5. Parsing of unstructured data can be easily carried out

2. Logcheck
Logcheck is a full platform to monitor and control your system. It helps a system administrator to Identify unknown problems that occurs automatically in Log-files. During configuration the system administrator provides with an email address such that all of the analysis report is automatically forwarded to this email ID on a periodic basis.
All of the Log system rebooting is done on an hourly basis that occur by default. Log-check enables with different layer of filtering done depending on the system. These are:
1. Paranoid: is maintain for high-security systems where the services that runs are very less in number.
2. Server: this is the default filtering level for log-check and its rules are defined accordingly to different systems.
3. Workstation: it is for sheltered systems and helps to filter most of the messages. It also includes rules defined under paranoid and server levels.
3. ClearOS Log Viewer
The powerful Log Viewer by ClearOS serves something more than just log management – it keeps your system safe and also checks system status and health. Need to manage huge log files, no issue. ClearOS Log Viewer is capable of handling and reviewing large databases with great precision. It shows a tabular display of all log files in your system, making the search process easy for you.

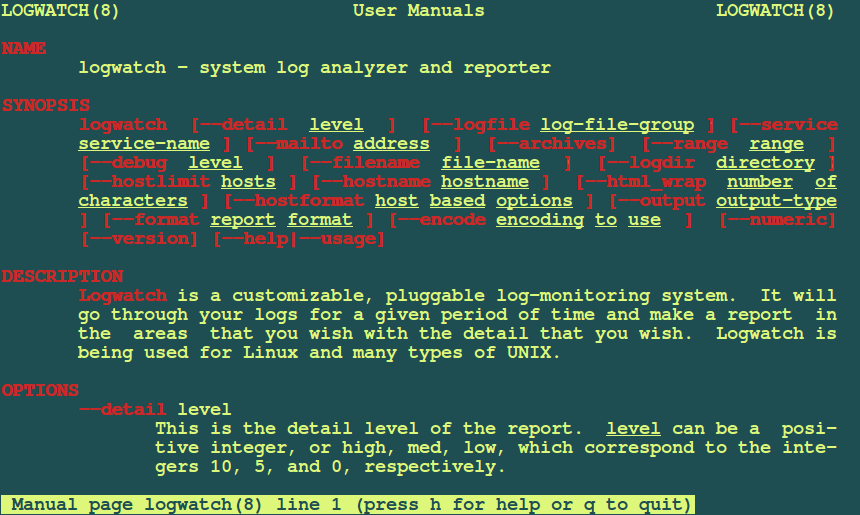
4. Logwatch
Logwatch is an easily customizable Open Source Log management tool that carries out features such as reviewing Log files for a given period of time and then generating report for the same based on the areas set by the administrator itself. That is one only need to set up his own information area.
One of the most essential features of this logging system is that it is easy to use for new System Administrator and it also works on most Linux distributions available and many Unix systems.
It enables a system administrator to add additional plug-ins, create custom scripts that serve specific logging needs.

5. Logstash
Just like the other open source Log management tools available on Linux defined above, Logstash resembles its own functionality of Real-time pipelining. As it was originally intended to maintain data collection but if we told about the new updated version integrated with several other features that collects a wide range of input data formats, works as an Open Source Filter and also output plug-ins and formats.
Logstash also allows System Administrators to cleanse, compare and standardize all their logging data for distinct advanced analytics and also create visualization use cases as well.