One of the many benefits of open source software is that it offers some protection from having programs disappear or stop working. If part of a platform changes in a non-compatible way, users are free to modify the program so that it continues to work in the new environment. At a level above the software, open standards protect the information itself. Everybody expects to be able to open a JPEG image they took with their digital camera 5 years ago. And, it is not unreasonable to expect to be able to open that same image decades from now. For example, an ASCII text file written 40 years ago can be easily viewed today.
Many formats exist for storing text documents with rich markup, spreadsheets, and presentations, and the Open Document Format (ODF) is an open standard describing how office documents are stored in files. Many applications support the ODF standard including LibreOffice, OpenOffice, Calligra, AbiWord, WebODF, Google Docs, and Microsoft Office.
Having an office file standard is all well and good. For this to be useful, however, you have to be able to see how well various office applications support it. Knowing that many applications are dedicated to supporting — and improving their support for — a file standard is a good way to try to ensure that the office document you save today can be properly opened in 40 years’ time.
Officeshots and ODFAutoTests provide insight into how various office applications on various platforms deal with ODF files. With these tools, you can see if a particular feature will be presented properly when using an office application that you do not have a license for on an operating system that you are not running. You can also see how well a feature of the format is currently supported, and what minimal version of software is needed so that you do not lose features when you update an office file.
Officeshots
Not every application implements a standard to the same level, which is important to know. For example, a mobile app might only allow you to capture paragraphs with text formatting such as bold, italic etc. Thus, if you try to load a more complex document, you will be aware that some information will likely be lost by the app.
The Officeshots.org website lets you upload a document and see how it will be rendered and saved with a variety of office suites. The office suites available can include those that you do not have access to and which run on operating systems that you are not using. Some office suites do not allow many versions to be installed at once. You might be interested in how an older (or newer) version of your favorite application handles a file you are working on.
With Officeshots, you can define a project or company-wide standard regarding which ODF features are acceptable for use in documents. Thus, you can ensure that everybody who might be opening these files — with a minimal version of a selection of office suites on various platforms — will be able to see the documents as they are intended to be seen (Figure 1).
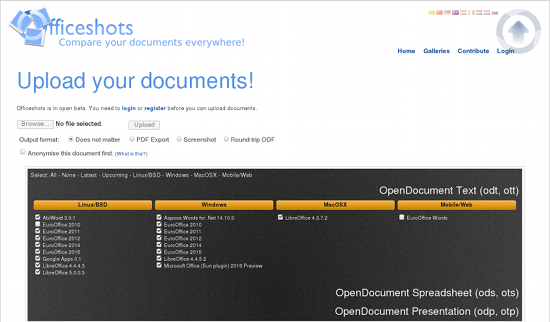
Using Officeshots is simple, you first register for an account — just name, email, and password are required. The home page for Officeshots then allows you to upload an ODF file, and you can select which applications you want to load it with. You can also select whether you would like those applications to save back to an ODF or whether you would like a PDF showing how each program presents the ODF you have uploaded (Figure 2).
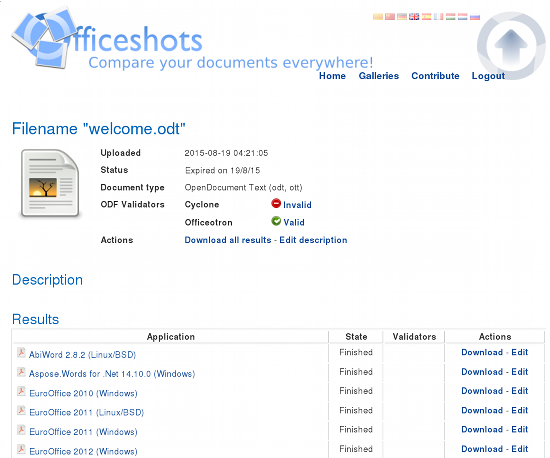
The Officeshots server itself is open source software. So, you could set up your own personal server if you do not wish to upload your ODF files to the main Officeshots server. If you would like to help the Officeshots project, you can run an Officeshots Factory. The factory is responsible for taking a document and processing it in a specific version of a specific office application.
The processing normally involves loading and saving the ODF or generating a PDF from the given ODF file. Recently, a script was introduced that can detect known office applications and set up the factory configuration file for you. It is hoped that the factory setup process will be further slip-streamed in the future. The more people and organizations contribute, the more useful the service will become for all.
ODFAutoTests
Officeshots is great if you want to see how a specific ODF will appear to a user or if you want to examine the output ODF file that the application will produce when saving an update to the file. On the other hand, you might like to quickly be able to see if a feature is supported in a specific application, such as LibreOffice 4.3.x. The ODFAutoTests project aims to provide a methodical test of each attribute for each important document element for many versions of many office suites.
Currently, about 10 major document elements are included in the test results. For each feature tested, a screenshot of how that feature renders is presented along with an investigation into the output ODF produced and whether that feature has been preserved in the output document (Figure 3).
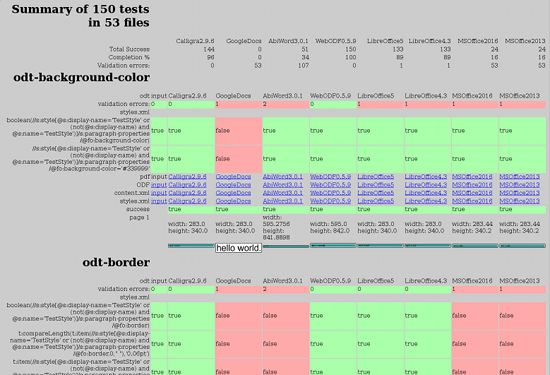
Some projects like WebODF aim first and foremost for clean document preservation. So, although a feature might not currently render in WebODF, for example, the information will be preserved when you save the ODF file back to disk. For a different application, however, you might see that something appears to render properly — for example, you may see a background color in the screenshot — but that background information is not preserved when you save an ODF from the application.
The ODFAutoTests project will likely be expanded to include more features, including the preservation of RDF inside ODF files. With the right application support, embedding RDF inside of ODF files has the potential to bring the Semantic Web to everybody through document computing. It is also planned to have ODFAutoTests use Officeshots to perform the tests, so the range of office suites tested will be greatly expanded in the future.
Final Words
Some ODFAutoTest results show that contemporary office applications lack support for many interesting features of ODF. This is both good and bad news. It is currently bad in that some features will require recent versions of specific applications to be preserved. However, it is good news because discovering which features could be improved in various applications allows developers to know which areas to work on for the next release. Knowing exactly what to improve and understanding the expected outcome are two golden pieces of information for software developers.
You might be interested in the Officeshots factory code even if you have no intention of running a factory yourself. With the factory code, you can run document conversions to ODF and PDF from the command line. This conversion can use any software that you have configured your factory to use — such as, using Google Docs to render and ODF file to a PDF. This allows you to know how an email recipient, for example, will see a file if they open it in Google Docs.
If you are writing software that processes ODF files or are concerned about preserving ODF files, you might additionally be interested in attending the ODF Plugfest. Perhaps future Plugfest events will open up the ODFAutoTest results to include problematic sample ODF files that have caused issues with specific versions of office applications in the past. If a particular ODF feature is a little bit tricky, it is likely to be an issue in more than one office application.
 Happy Ada Lovelace Day! Please join us in commemorating the life of Ada Lovelace by celebrating the achievements – past and present – of women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Happy Ada Lovelace Day! Please join us in commemorating the life of Ada Lovelace by celebrating the achievements – past and present – of women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.



 ONOS’ community and The
ONOS’ community and The  The Document Foundation has revealed that the first Release Candidate for the LibreOffice 5.0.3 branch has been released and is now available for download.
The Document Foundation has revealed that the first Release Candidate for the LibreOffice 5.0.3 branch has been released and is now available for download.
 After building up its Node.js expertise with its StrongLoop acquisition, IBM has added Node.js debugging capabilities to its Bluemix PaaS.
After building up its Node.js expertise with its StrongLoop acquisition, IBM has added Node.js debugging capabilities to its Bluemix PaaS.